1. Why This Speed Battle Matters More Than You Think
Have you ever found yourself waiting endlessly because of files taking too long to move off your external drive? You’re not alone. The speed of USB-C versus USB 3.0 can literally save you hours of waiting time, and which port type you use can change how you work every day USB cable.
The big question here is How much faster is USB-C in reality? You will be surprised by the answer regarding USB speeds. USB-C is capable of data transfer rates 20 times higher than USB 2.0 and about 67 times higher than SATA III – but there’s more to it than that usb devices.

In this modern, rapid digital world, every second matters. You need not only technical knowledge, but productivity superpower: whether you need to back up terabytes of data, move 4K video files, or even just transfer documents between machines, you need to understand connectivity speeds, especially when using a usb type c connector usb connector.
Now, we will zero in on an in-depth, data-driven comparison of data transfer speed and make the most intelligent connectivity decision based on your own needs and budget usb power delivery.
2. Understanding the USB Evolution Timeline

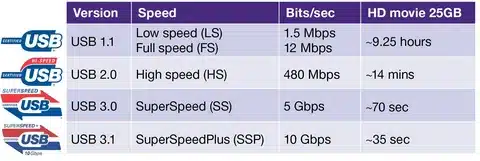
The question is how we ended up where we are today in terms of the usb standards and then we can proceed into the comparisons of the speeds. USB has experienced a fantastic development since the 1990s, when it was initiated. The grave advancement was characteristic of the two generations in the pace of transferring information, the amount of essentiality that can be conveyed, and usability in overall USB 3.2 Gen 2.
The revolution started with USB 1.1 with 12 Mbps speeds that were regarded as light speed when compared with serial and parallel ports. USB 2.0 multiplied that speed forty-eight times to 480 Mbps. That was followed by the game-changer USB 3, now called USB 3.1 Gen 1, and it has a speed of 5 Gbps-over 10 times higher than the old one.

USB-C is the most recent USB type connector standard in USB technology, although it is worth pointing out that USB-C is the physical connector, whereas the speed is determined by which version of the USB protocol it implements USB capabilities.
3. Speed Comparison: The Complete Performance Breakdown
| Interface / Generation | Max Speed | Real-World Speed | Notable Comparison |
| USB 1.1 | 12 Mbps | ~1.5 MB/s | Baseline |
| USB 2.0 | 480 Mbps | ~60 MB/s | ~20× faster than USB 1.1 |
| USB 3.0 / 3.1 Gen 1 | 5 Gbps | ~625 MB/s | Big leap over USB 2.0 |
| USB 3.1 Gen 2 (USB-C) | 10 Gbps | ~1,250 MB/s | Sweet spot performance |
| SATA III | 6 Gbps | ~750 MB/s | USB-C ≈67% faster |
| Thunderbolt 1 | 10 Gbps | ~1,250 MB/s | Same as USB-C |
| Thunderbolt 2 | 20 Gbps | ~2,500 MB/s | ≈2× faster than USB-C |
| Thunderbolt 3 / 4 or USB4 | 40 Gbps | ~5,000 MB/s | ≈4× faster than USB-C |
Speed Spotlight: USB-C (USB 3.1 Gen 2) provides 10 Gbps theoretical speed with a real-world throughput of approximately 1250 MB/s-that is 20x faster than USB 2.0 and 67% faster than the traditional SATA III connections.
4. Real-World Speed Tests: Theory vs Practice
On paper, the theoretical speeds sound impressive, but in practice, they are a different story. In optimum conditions, USB-C connections can reach 70-80 percent of their theoretical maximum speeds. That is to say, your 10 Gbps USB-C connection will probably run approximately 7-8 Gbps in practice a power outlet.

Real transfer rates depend on several factors, including the quality of the cables being used, the capabilities of the device to be used, file system overheads, and background processes. The reason why real USB-C is always more handy in the field than its predecessors is that it is a convenient alternative to the user who needs to transfer information via USB in a secure manner, not to mention a high-speed manner.
Big file transfer testing proves that the USB-C can complete the task within 30 seconds, which may require 10 minutes using USB 2.0. This fundamental transformation gets rid of the means we use to share data with external memory and peripherals.
5. Cost-Effectiveness: Performance Per Dollar Analysis
This is the point at which USB-C really excels in the marketplace: tremendous value-to-money. USB-C solutions are about 75 per cent cheaper than comparable solutions utilizing Thunderbolt and provide performance levels that meet the everyday computing demands of most users.
Though it will cost under 15-25 dollars more to buy a quality USB-C cable of 10 Gbps capability, whereas a similar Thunderbolt 3 cable will cost 50-80 dollars. External drives have USB-C solutions that are between 30 and 50 dollars more affordable than Thunderbolt alternatives, which cost between 100 and 150 dollars.
The value proposition is obvious: Professional-level speed at consumer prices. USB-C provides high-quality performance at affordable prices to businesses with IT budgets to manage and consumers who are assembling home systems.
6. Large File Transfer Scenarios: When Speed Matters Most

The speed advantage can be immediately felt in cases where files have to be moved via the USB-C. A 100GB 4K video project will take approximately 13 minutes to transfer using USB-C and 22 minutes to transfer using SATA III–a 9-minute improvement in time-saving per transfer.
The difference is further increased for the photo shooters who deal with the RAW files. A typical wedding shoot that spits out 50GB of photo data takes less than 7 minutes on USB-C, nearly 12 on the old USB 3.0 connections.
USB-C is significantly faster than USB-A with database backups, system imaging, and bulk media transfers. These minutes saved accumulate throughout the working day, so the introduction of USB-C is a productivity multiplier.
7. Gaming and Entertainment Applications
Gaming today demands storage capability to extreme levels. USB-C external drives offer almost internal storage capability of a game laptop and game console. Installation of the games is also much faster with USB-C at the point of connection.
USB-C speed is incredibly valuable to streaming content creators and even to cell phones to transfer recorded gameplay (especially in 4K). One average 2-hour 4k gaming session captures 20-30GB of footage–USB-C is capable of transferring this in less than 4 minutes, which is much faster than the previous standards, which could take 8+ minutes.

USB-C connections allow music producers who create with high-resolution audio files and huge sample libraries to remove bottlenecks that once slowed down creative workflows.
8. Professional Video Editing: The Creative Professional’s Perspective
Video professionals are the most challenging users of USB-C. 4K workflows today produce massive files that tax storage systems. USB-C offers enough bandwidth to ensure timeline scrubbing and preview of real-time effects.
USB-C is especially good at color grading workflows. Video loading, effects, and rendered outputs are much quicker than on the previous generation connections. This acceleration is directly related to savings in billable hours on the side of professional editors.
Even greater file sets are created with multi-camera productions. USB-C allows powerful multicam sync operations, which would be agonizingly slow under earlier connection specifications.
9. External SSD Performance: Maximizing Portable Storage
USB-C is becoming a common method of data transfer, charging, and display output on Smartphones. The latest smartphones utilize advanced usb ports, consuming a lot of information with high-resolution images, recording 4K video clips, and installing huge applications.

USB-C allows a rapid process of phone backup and file transfer. Transferring videos and photos between phones and computers will not be as tedious as it always is. Speed will enable more backups to ensure better data security.
USB-C speed is particularly a welcome feature among professional photographers who use smartphones to generate content and subsequently utilize those photos to edit them on a desktop computer.
10. Mobile Device Integration: The Smartphone Revolution

Forward compatibility and more features are the philosophy of USB-C, as opposed to micro USB. An array of protocols and standards is compatible with existing USB-C solutions, meaning they can last longer as technology changes.
Future-ready specifications will consist of USB4 host/host (up to 40 Gbps) and USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 (up to 20 Gbps) host/host (up to 20 Gbps with DisplayPort 2.1), DisplayPort Alt Mode (up to 80 Gbps) power delivery up to 240W over USB (PD 3.1).
This interoperability will allow the USB-C investment to continue changing standards. Unlike other connector generations, the flexible design of USB-C can meet the requirements of the future.
11. Future-Proofing: USB-C’s Expanding Capabilities

The quality of USB-C cables has an important impact on performance. Low-priced cables do not support full 10 Gbps data rate speeds because of poor shielding, bad conductors, or poor quality or construction. Good manufacturers of cables offer quality cables that provide rated functions.
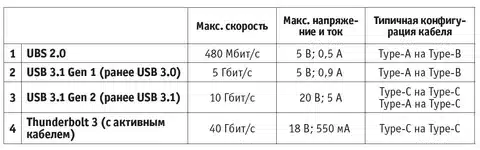
At longer lengths, the differences between active and passive cables are significant. Active cables have signal boosters that allow full-speed operation at ranges where passive cables can no longer work. Active cables are used to provide reliable high-speed performance to installations that have cables exceeding 2 meters in length.
There are certification programs, such as USB-IF certification that are used to determine cables that meet official specifications. Certified cables are a guarantee of performance and safety.
12. Cable Quality Impact: Why Not All USB-C is Equal

USB-C supports Power Delivery features that are changing how devices are charged and used. USB-C can deliver up to 240 W of power to charge laptops and monitors, and any other high-power device simultaneously, and can also deliver data at the fastest rate achievable.
This is a two-fold capability that eliminates cable messaging and simplifies installation. Power-high-speed-data single-cable solutions are handy and simplify the desk.
The technique that will offer the best prices on the associated devices is Power Delivery negotiation. Smart power control means no overcharging is permitted as much as possible, and transfer rates are maximized as much as possible.
13. Power Delivery Revolution: Beyond Just Speed

The popularity of USB-C does not mean that it is universally compatible. Not every device supports the high speeds provided by the modern connector, and some USB-C ports are only USB 2.0 despite the modern connector that is used, which is based on the data transfer standard.
Do not assume that the connector type is a measure of performance. Some low-end devices have also integrated USB-C connectors and USB 2.0 controllers, which do not provide speed benefits but are convenient today.
USB-C devices that are backward compatible can be used with older standards with appropriate adapters, but will also be limited to the lowest common denominator in a mixed configuration.
14. Compatibility Considerations: Making Smart Choices

USB-C (USB 3.1 Gen 2): The Universal Hero is compatible with the majority and will not be quite expensive. Leading in daily file transfer, external storage, mobile devices and moderate content creation. It is future-ready and has a great price-performance ratio.
Internal Specialist, SATA III.
Good over internal desktop/laptop connections, but weak over external connections. Not as versatile as USB-C with regard to the current multi-device workflow.
Thunderbolt 3 / 4 USB4: The Workhorse. The one you require to construct a high-power workflow and the utmost bandwidth. Superset Perfect in 4K video editing, Multi-monitors, daisy-chaining of devices, high-performance computing, and supersets. Premium pricing is an expression of premium capabilities.
15. The Final Verdict: Choosing Your Ideal Connection
USB-C (USB 3.1 Gen 2): The Universal Champion Won’t The Universal won’t be very expensive. Best in everyday file transfer, external storage, connection with wireless gadgets, and average content generation. Has a tremendous price-to-performance ratio and is future-proof.
Thunderbolt 3/4 & USB4: The Professional Workhorse. The one that you need to enable the most intensive professional workflow with the highest bandwidth.
Good on internal desktop/laptop connections, but poor on external connections. Not as flexible as USB-C in regard to the current multi-device workflow.
Thunderbolt 3/4 & USB4: The Workhorse One you need to practice serious professional activity and the highest bandwidth. Supersets are Optimal in 4K video editing, multi-monitors, device daisy-chaining, and high-performance computing. The premium pricing indicates the premium capabilities.
Quick Decision Framework:
- Day-to-day computing + cost-effective → USB-C
- Creative work (professional) unlimited budget → Thunderbolt/USB4
- Internal desktop storage + cost optimization → SATA III
- Mobile integration + versatility → USB-C
Frequently Asked Questions
Is USB-C always faster than USB-A? No–the connector shape has nothing to do with speed but the underlying USB protocol. A USB-C port based on USB 2.0 will be slower than a USB-A port based on USB 3.1. Never assume what equipment can actually do.
Do I need Thunderbolt if I just want quick backups?
USB-C is much faster and costs far less in most backup cases. Thunderbolt is much more attractive to professional video editing, daisy chains of devices, or where high speed justifies high cost.
Conclusion: The Smart Choice for Modern Computing
According to the USB Implementers Forum, USB-C will be the new standard that brings the best of both worlds with 10 Gbps professional capabilities at affordable consumer prices. USB-C offers outstanding value in most computing applications, with real-world performance 67 times faster than SATA III and 75 percent lower cost than Thunderbolt options.
High-speed data transfer, compatibility with all types of devices, and future-proof design make USB-C the smart choice when people are building systems that are destined to be used in the years to come.
USB-C provides the bandwidth and the flexibility required to support existing systems and meet future demands effectively, whether it comes to upgrading established systems or designing a new system.