Introduction: What Is SDI?
Serial Digital Interface (SDI) is a professional video transmission standard that has changed the broadcasting industry. The technology also allows uncompressed digital video and audio signals to be transmitted over coaxial cable or fiber-optic cable with unprecedented quality extending to all regions of the signal chain.
SDI was originally standardized by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) in 1989, but soon became the workhorse of professional video production. It is still important today in professional broadcasting, live events, and high-quality video production settings where the quality and reliability of the signal are of utmost concern.
Key Features of SDI
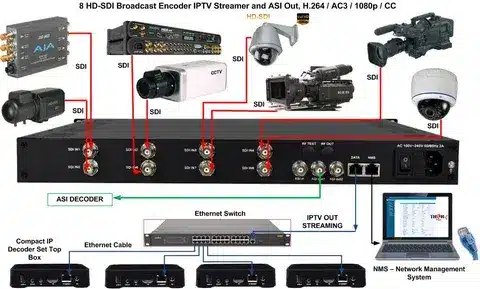
SDI technology has some unique features, which render it essential in professional video usage:
Uncompressed Transmission The biggest advantage of SDI is probably Uncompressed Transmission. SDI maintains all the bits of information that the source provided, unlike consumer-grade connections which tend to compress video data, allowing video and audio quality to be as clean as possible in the signal path. This attribute is critical in professional processes where no quality can be compromised.
Low Latency SIO is best suited to live broadcasting and real time use due to Low Latency. The near-zero input/output lag means that live events, news shows and interactive productions can run without any perceived latency to affect viewer experience or production timing delay.
Error Detection SDI standards have Error Detection features that include advanced facilities to check signal integrity in real-time. It is a feature that allows tracking and fixing the transmission problems before they manifest as a problem, and it keeps the broadcast quality even in the most difficult settings.
Versatility enables the SDI to accommodate different resolutions and frame rates, both in standard definition and ultra-high definition formats. This flexibility keeps the investment in equipment useful as the technology standards change.
SDI Standards Evolution

The history of the development of SDI standards reflects the incessant demand of the broadcast industry for higher quality and resolution:
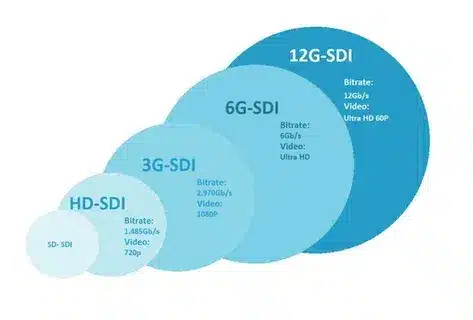
SD-SDI (Standard Definition SDI) The original implementation, SD-SDI (Standard Definition SDI), was released in 1989, and enabled standard definition video at 270 Mbps. It is this fundamental standard that defined the reliability and quality features of all subsequent SDI developments.
HD-SDI (High Definition SDI) HD-SDI (high definition SDI) was developed to accommodate the high-definition video formats, especially 1080i and 720p at 1.485 Gbps. This development facilitated the move to high definition broadcasting without the compromise in uncompressed quality that the professionals required.
3G-SDI SDI 3G was designed to support video at 1080p and with high frame rate of 2.97 Gbps. This standard was essential to progressive scan broadcasting as well as high-frame-rate production work.
6G/12G/24G-SDI standards that were to handle 4K and higher, and with significantly higher bandwidth. The standards allow ultra-high-definition production workflows with the reliability features of previous SDI implementations.
UHD-SDI (Ultra High Definition SDI) is designed to specifically support 4K video transmission requirements and will help the broadcast industry to provide viewers around the globe with the latest visual experiences.
Applications of SDI
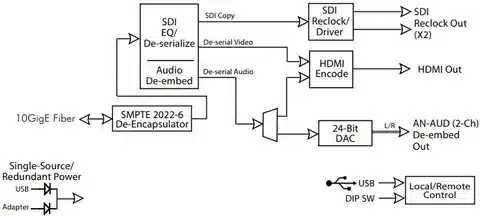
SDI technology is widely used in a variety of professional video applications:
Broadcasting The most common use application is broadcasting, in which cameras, video switchers, servers, and other devices are connected to SDI at various locations around television studios and production facilities. The technology is reliable and of quality to be installed in on-air operation where failure is not an option.
Live Events use SDI to live stream concerts, sports events, conferences and other real-time productions. The reason is that the low latency and high quality provide the audience with the best viewing experience either in person or remotely.
Medical Imaging In diagnostic applications, Medical Imaging applies SDI to transmit high-resolution video. The transmission is without compression so that vital visual information is not lost to imprecise medical interpretation and consultation.
Security Systems Security Systems SDI has minimal latency in its surveillance applications where real-time is important. The technology is reliable and can constantly operate in high-security situations.
Benefits of Using SDI
The benefits of installing SDI technology are far more than simple functionality:
High-Quality Transmission maintains the original video and audio quality along the signal path. Professional uses of this attribute must be considered, where fidelity to the visuals is directly related to the value and functionality of the final product.
Reliability The reason is that SDI is also reliable because it is resistant to electromagnetic noise and signal loss. Professional settings tend to be full of electronic equipment which may disrupt video signal, but SDI design reduces these fears.
Future-Proofing will allow SDI infrastructure to keep up with changing broadcast standards. Updating and upgrading existing SDI installations can often be done instead of being completely replaced as the number of features needed increases and as the requirements to solve them increase.
Cost-Effectiveness is realized with the help of the standard 75 ohm coaxial cables that are quite common and also affordable. This affordability makes infrastructure affordable, but still professional level.
SDI vs. HDMI: A Quick Comparison
Understanding the differences between SDI and HDMI helps clarify when each technology is most appropriate:
| Feature | SDI | HDMI |
| Compression | Uncompressed | Compressed |
| Cable Length | Long-distance (up to 300m) | Short-distance (up to 10m) |
| Use Case | Professional broadcasting | Consumer electronics |
| Connector Type | BNC | HDMI |
| Signal Integrity | Superior over long distances | Limited by cable length |
| Cost | Professional-grade pricing | Consumer-friendly pricing |
How to Set Up an SDI Workflow
A successful SDI workflow is a matter of planning and implementation:
- Choose the Right SDI Standard Select the Right SDI Standard according to your particular resolution requirements and transmission distance requirements. This decision should be made in view of future expansion opportunities lest it becomes an early upgrade.
- Select Compatible Equipment: Choose Compatible Equipment by checking that cameras, monitors, switchers, and other equipment of interest meet your desired SDI standard. Compatibility can create bottlenecks in the workflow that affect the effectiveness of the whole workflow.
- Connect Using Appropriate Cables Connect With the Right Cables would involve spending money on good-quality coaxial or fiber-optic cables that fit the requirements of your selected SDI standard. The quality of the cable has a direct relationship with signal integrity and system reliability.
- Test the Setup Check signal integrity, latency, and the performance of the entire system. Extensive testing is used to detect possible problems before they affect production processes.
The Future of SDI
SDI technology is still developing to suit the new requirements of the industry:
Integration with IP Networks is an important direction as the industry moves to IP-based workflows. This development provides increased route flexibility and distribution and may preserve the quality benefits of SDI.
Higher Resolutions promote ongoing progress as 8K and other resolutions are increasingly common in broadcasting and production settings. SDI standards will remain flexible to these emerging demands.
Enhanced Compression Techniques are under development that strike a balance between quality preservation and bandwidth saving. Such innovations will enable the next generation of SDI implementations to operate at even higher resolutions across existing infrastructure.
Conclusion
One cornerstone technology in professional video production that has never been superseded by any alternative because of its unparalleled quality, reliability, and versatility is the Serial Digital Interface. It is an important aspect of broadcasting, live events, medical imaging, and security systems because it detects errors with high reliability, provides a low-latency transmission, a nd uncompressed transmission of information.
The industry continues to evolve into more sophisticated solutions and more complex production systems, and therefore, the capabilities, functions, and uses of SDI are further gaining value to video production and broadcast specialists. The successful history of the technology and its further evolution make it definite that it will not become outdated when new issues and opportunities of the digital media world emerge.
SDI technology can provide the high quality and consistency that a professional user requires, or you merely desire to get to know even more concerning what professional video transmission standards are, or whether or not to update a broadcast station, set up a live occasion like a production system, or you merely wish to discover even more.

