Introduction: Why USB-C and USB 3.1 Matter in Today’s Tech World
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, connectivity standards play a crucial role in determining how efficiently our devices communicate and transfer data. Among the most significant developments in recent years are USB Type-C connectors and USB 3.1 data transfer standards, two technologies that have revolutionized the way we connect and charge our devices according to the usb specification .

Understanding the distinction between these technologies, such as the usb port similarities, is essential for anyone looking to make informed decisions about their tech purchases or upgrades, especially when choosing usb if certified product . While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different aspects of connectivity – one focusing on the physical connection, the other on data transfer capabilities.
The Critical Importance of Modern Connectivity Standards

As our digital lives become increasingly complex, with multiple devices requiring seamless integration, the importance of standardized, high-performance connectivity for connected devices cannot be overstated. Modern users demand faster data transfers, more reliable connections, and simplified charging solutions that work across multiple device types, including various peripheral devices .
USB Type-C and USB 3.1 technologies address these needs by providing enhanced performance, improved user experience, and future-ready capabilities that support emerging technologies. These standards, including usb pd, are not just incremental improvements – they represent a fundamental shift toward more efficient, versatile connectivity solutions.
What is USB Type-C? Understanding the Physical Connector Revolution

Defining the USB Type-C Standard
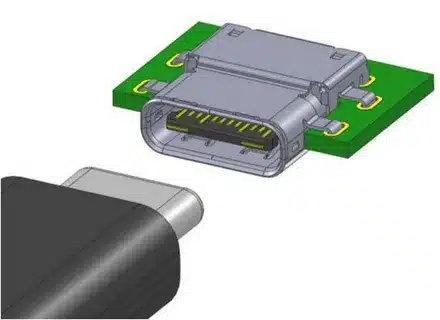
USB Type-C, officially known as USB-C, is a 24-pin USB connector system distinguished by its distinctive oval-shaped receptacle and plug. Introduced in 2014, this connector standard was designed to eventually replace all other USB connector types, creating a universal solution for device connectivity, often referred to as a universal connector .
The development of USB Type-C emerged from the need for a more versatile, durable, and user-friendly connector that could handle the increasing power and data requirements of modern devices. Unlike its predecessors, USB-C was engineered from the ground up to support multiple protocols and higher power delivery capabilities, making it compatible with existing usb technolog .
Revolutionary Design Features of USB Type-C

The reversible design stands as one of USB-C’s most celebrated features. Unlike traditional USB connectors that require specific orientation, USB-C plugs can be inserted either way, eliminating the frustration of multiple connection attempts. This seemingly simple improvement over traditional usb cables has significantly enhanced user experience across millions of devices worldwide.
The compact form factor of USB-C makes it ideal for increasingly thin laptops, smartphones, and tablets. Measuring just 8.4mm by 2.6mm, it’s smaller than type a connectors while providing superior functionality. This size reduction has enabled manufacturers to create slimmer device profiles without compromising connectivity options.
Power Delivery Capabilities That Changed Everything

USB Type-C supports the USB Power Delivery (PD) specification, enabling power transfer up to 100 watts in standard implementations. This capability allows USB-C to charge everything from smartphones to high-performance laptops using a single cable type, revolutionizing how we think about device charging.
The intelligent power negotiation built into USB-C ensures devices receive optimal charging speeds while maintaining safety standards. This smart charging capability, supported by superspeed usb, has made USB-C the preferred choice for manufacturers seeking to simplify their product ecosystems.
Common Applications Across Device Categories
USB Type-C has found widespread adoption across numerous device categories. In smartphones, flagship models from major manufacturers have transitioned to USB-C, offering faster charging and improved data transfer capabilities compared to previous usb generations and older equipment, like micro-USB implementations.
Laptop manufacturers have embraced USB-C for its ability to handle power delivery, data transfer, and even video output through a single port. Many modern laptops feature multiple USB-C ports, some serving as the primary charging interface while others provide connectivity for peripherals, docking station, and external displays.
Understanding USB 3.1: The Data Transfer Standard Evolution

Comprehensive Overview of USB 3.1 Technology
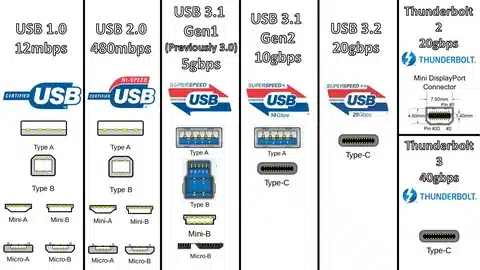
USB 3.1, introduced in 2013, represents a significant advancement in USB data transfer standards. This specification doubled the theoretical maximum data transfer rate from USB 3.0’s 5 Gbps to an impressive 10 Gbps, while also introducing enhanced power delivery capabilities and improved data encoding methods.
The development of USB 3.1 was driven by the increasing demands of high-resolution content, large file transfers, and power-hungry devices that required more efficient data and power delivery. This standard laid the groundwork for many of the advanced connectivity features for electronic devices we take for granted today.
Key Technical Features and Improvements
USB 3.1 introduced several technical improvements over its predecessors. The enhanced SuperSpeed+ mode provides theoretical data transfer rates up to 10 Gbps, making it suitable for professional applications, including alt modes, requiring rapid file transfers, such as video editing and large database operations.
The improved power delivery specifications in USB 3.1 support up to 20 volts and 5 amperes, enabling 100-watt power delivery that can charge laptops and other high-power devices. This capability, being backward compatible, eliminated the need for separate power adapters in many applications.
Enhanced Power Delivery and Efficiency
Beyond raw power numbers, USB 3.1 introduced more intelligent power management. The standard includes provisions for power negotiation between devices, ensuring optimal charging speeds while maintaining safety standards, especially when you need to transfer data . This negotiation process allows type b devices to communicate their power requirements and capabilities automatically.
The enhanced efficiency of USB 3.1’s power delivery system reduces energy waste during charging and data transfer operations. This improvement, especially with usb cables, is particularly important for battery-powered devices where energy efficiency directly impacts usage time and battery longevity.
Evolution to USB 3.2: Understanding the Rebranding
The USB Implementers Forum later rebranded USB 3.1 as part of the USB 3.2 specification to create a more coherent naming structure. USB 3.1 Gen 1 became USB 3.2 Gen 1, while USB 3.1 Gen 2 became USB 3.2 Gen 2, with each generation offering specific performance characteristics.
This rebranding, while potentially confusing, was intended to provide clearer differentiation between performance levels and help consumers make more informed purchasing decisions. Understanding these designations, often highlighted in marketing materials, is crucial for anyone seeking to maximize their device’s connectivity performance.
The Relationship Between USB Type-C and USB 3.1: Clearing the Confusion

Physical Connector vs. Data Transfer Standard
One of the most important distinctions to understand is that USB Type-C refers to the physical connector shape and size, while USB 3.1 (now USB 3.2) refers to the data transfer protocol and speed capabilities. These are two separate specifications that can work together but are not inherently dependent on each other.
A device can have a USB Type-C port that supports USB 2.0 speeds, USB 3.0 speeds, or USB 3.1/3.2 speeds, depending on the implementation chosen by the manufacturer. This flexibility allows manufacturers to balance cost, performance, and design requirements based on their target market and use cases.
Compatibility Considerations Across Implementations
Not every USB Type-C port automatically supports USB 3.1 speeds or capabilities. Some budget devices may feature USB-C connectors that only support USB 2.0 data transfer rates to reduce manufacturing costs. This implementation provides the convenience of the reversible connector without the higher-speed capabilities.
When purchasing devices or cables, it’s essential to verify the specific USB standard supported by each port. Product specifications should clearly indicate whether a USB-C port supports USB 3.1/3.2 speeds, power delivery capabilities, and other advanced features.
Common Misconceptions and Reality Checks
Many consumers assume that all USB-C cables and ports are created equal, leading to disappointing performance when expectations don’t match reality. The truth is that USB-C is simply a connector type, and the actual capabilities depend on the underlying implementation and cable quality.
Some devices may have USB-C ports that support different standards on the same device. For example, a laptop might have one USB-C port optimized for charging and power delivery, while another focuses on high-speed data transfer, and a third supports video output.
Consumer Benefits: How USB-C and USB 3.1 Improve Daily Tech Use

Simplified Connectivity and Universal Compatibility
For everyday users, the combination of USB Type-C connectors and USB 3.1 speeds creates a significantly improved experience. The reversible connector eliminates the frustration of incorrect insertion attempts, while the increased data transfer speeds make file transfers, backups, and synchronization much faster.
The move toward USB-C standardization means fewer different cables and adapters cluttering desks and travel bags. Many users can now charge their laptop, smartphone, tablet, and other devices using the same USB-C cable, simplifying both home and travel setups.
Faster Data Transfer for Content Creators
Content creators working with large files benefit enormously from USB 3.1’s improved transfer speeds. Video editors can move 4K footage between devices in a fraction of the time required with older USB standards, improving workflow efficiency and reducing project timelines.
Photographers dealing with high-resolution RAW files find that USB 3.1 speeds make importing and backing up photos much more manageable. What once took hours can now be accomplished in minutes, allowing more time for creative work rather than file management.
Enhanced Charging Speed and Convenience
The power delivery capabilities of USB-C combined with USB 3.1’s power management create faster, more efficient charging experiences. Many smartphones now support rapid charging speeds that can provide hours of usage from just minutes of charging time, along with additional features .
Laptop users particularly benefit from USB-C charging, as many modern laptops can be charged using the same ports used for data transfer and peripheral connections. This consolidation reduces the number of ports and cables required, contributing to cleaner, more organized workspaces.
Manufacturing Advantages: Industry Benefits of Modern Standards

Standardization Reducing Production Complexity
For manufacturers, the adoption of USB Type-C and USB 3.1 standards offers significant advantages in terms of production standardization. Rather than designing and manufacturing multiple connector types for different device categories, companies can focus on optimizing their USB-C implementations to create full featured usb product .
This standardization reduces inventory complexity, as manufacturers need to stock fewer different connector types and cable variants. The reduced variety also simplifies quality assurance processes and reduces the potential for compatibility issues between products.
Design Flexibility and Device Miniaturization
The compact size of USB-C connectors enables manufacturers to create thinner devices without sacrificing functionality. This capability is particularly important in the competitive smartphone and laptop markets, where device thickness is often a key differentiating factor.
The versatility of USB-C also allows manufacturers to reduce the total number of ports required on devices. A single USB-C port can handle charging, data transfer, video output, and peripheral connections, freeing up space for other components or contributing to overall device miniaturization.
Future-Proofing and Technology Integration
By adopting USB-C and USB 3.1 standards, manufacturers position their products to support future technological developments. These standards provide a foundation for emerging technologies and protocol updates without requiring fundamental hardware changes.
The broad industry support for these standards ensures that manufacturers investing in USB-C and USB 3.1 technologies are aligning with long-term market trends rather than betting on proprietary solutions that may become obsolete.
Understanding Cable Quality: Not All USB-C Cables Are Equal

The Critical Importance of Cable Specifications
One of the most significant considerations when working with USB Type-C and USB 3.1 is understanding that cable quality varies dramatically. While all USB-C cables may look similar, their internal construction and capabilities can differ substantially, affecting both performance and safety, especially in two lane operation scenarios .
High-quality cables designed for USB 3.1 speeds include additional shielding, higher-grade conductors, and more sophisticated internal circuitry to handle the increased data rates and power delivery requirements. Cheaper cables may lack these features, resulting in reduced performance or potential compatibility issues.
Power Delivery Limitations and Safety Concerns
Not all USB-C cables support the full 100-watt power delivery specification. Some cables are designed only for low-power applications like smartphone charging and may not safely handle the power requirements of laptops or other high-power devices.
Using an inappropriate cable for high-power applications can result in overheating, reduced charging speeds, or even potential safety hazards. Always verify that cables are rated for the specific power requirements of your devices and applications.
Data Transfer Rate Variations
Even among cables that physically fit USB-C ports, data transfer capabilities can vary significantly. Some cables may only support USB 2.0 speeds despite having USB-C connectors, while others support the full USB 3.1 specification with 10 Gbps transfer rates.
When purchasing cables for high-speed data transfer applications, look for explicit specifications indicating USB 3.1 or USB 3.2 compatibility. Reputable manufacturers will clearly label their cables with supported specifications and certifications.
Device Compatibility Challenges and Solutions

Legacy Device Integration
One of the primary challenges with USB-C adoption is compatibility with older devices that use different connector types. While adapters and dongles provide solutions, they add complexity and potential points of failure to connectivity setups.
Many users find themselves carrying multiple adapters to maintain compatibility with existing peripherals, storage devices, and other accessories. This transition period can be frustrating, particularly for users with significant investments in USB-A peripherals.
Cross-Platform Compatibility Considerations
Different manufacturers may implement USB-C and USB 3.1 capabilities differently, leading to varying levels of compatibility between devices from different brands, and issues may arise due to other protocols not being compatible . Some features may work perfectly between devices from the same manufacturer but encounter issues when used with third-party products.
Understanding these compatibility nuances is important for users building multi-device setups or working in mixed-manufacturer environments. Research and testing may be required to ensure all desired features work correctly across different device combinations.
Adapter Solutions and Limitations
While adapters can bridge compatibility gaps, they may introduce limitations in terms of data transfer speeds, power delivery, or feature support. Some adapters may not support the full capabilities of USB 3.1 or may introduce additional latency in data transfers.
High-quality adapters that maintain full feature support are available but typically come at premium prices. Users should factor these additional costs into their budget when transitioning to USB-C ecosystems.
Cost Considerations in the USB-C Transition
Premium Pricing for Advanced Features
Devices featuring USB Type-C connectors with full USB 3.1 capabilities often carry premium pricing compared to their counterparts with older connector types. This price differential reflects the advanced technology and additional capabilities provided by these modern standards.
For budget-conscious consumers, this premium can be a significant consideration when choosing between devices. However, the long-term benefits of faster charging, improved data transfer, and future compatibility often justify the additional upfront investment.
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
While USB-C devices may cost more initially, the total cost of ownership can be lower due to reduced need for multiple chargers, cables, and adapters, including for your flash drive . Users who can standardize on USB-C accessories may find their overall accessory costs decrease over time.
The improved durability and longer lifespan of quality USB-C cables can also contribute to lower long-term costs, as users need to replace cables less frequently than with older, more fragile connector types.
Value Proposition for Different User Types
For casual users who primarily charge devices and transfer occasional files, the premium for USB 3.1 speeds may not provide sufficient value to justify the additional cost. USB-C convenience alone may be the primary benefit for this user segment.
Professional users who regularly transfer large files, work with high-resolution content, or require fast charging capabilities will likely find the premium pricing justified by the significant productivity improvements and time savings.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Connectivity Standards
Adoption Trends Across Industry Segments
The adoption of USB Type-C is accelerating across all major device categories. Smartphone manufacturers have largely completed the transition to USB-C, while laptop and tablet manufacturers are rapidly following suit. Even traditionally conservative sectors like automotive and industrial applications are beginning to embrace these standards.
This widespread adoption creates a positive feedback loop where increased adoption drives down costs, making the technology accessible to more price-sensitive market segments and accelerating further adoption.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
USB Type-C’s versatility makes it an ideal platform for integrating emerging connectivity technologies. Standards like Thunderbolt 3 and 4 use USB-C connectors, providing even higher performance capabilities while maintaining physical compatibility.
The ongoing development of USB4 promises to bring Thunderbolt-class performance to standard USB implementations, further enhancing the value proposition of USB-C connectors and potentially making high-performance connectivity more accessible across device categories.
Technological Advancement Roadmap
Future developments in USB technology are likely to focus on increased data transfer speeds, improved power efficiency, and enhanced protocol support. These improvements will build upon the foundation established by USB Type-C and USB 3.1, ensuring continued relevance and capability expansion.
The industry’s commitment to backward compatibility means that investments in USB-C infrastructure today will continue to provide value as new capabilities are added through software and firmware updates.
Standardization Efforts and Universal Adoption
Industry Collaboration and Standards Development
The success of USB Type-C and USB 3.1 reflects extensive collaboration between major technology companies, regulatory bodies, and standards organizations. This cooperative approach has ensured broad compatibility and interoperability across different manufacturers and device types.
Ongoing standardization efforts focus on refining specifications, improving compatibility testing, and developing new capabilities while maintaining backward compatibility with existing implementations.
Regulatory and Market Forces
Government regulations in some regions are driving standardization toward USB-C for device charging, recognizing the environmental and consumer benefits of reduced connector variety. These regulatory pressures are accelerating adoption timelines and encouraging manufacturers to prioritize USB-C implementations.
Market forces also favor standardization, as consumers increasingly expect universal compatibility and simplified connectivity solutions. Manufacturers that fail to adopt these standards risk losing market share to more forward-thinking competitors.
Making Informed Technology Decisions
Evaluating Device Specifications
When purchasing new devices, carefully review the specific USB implementations supported by each port. Look for clear specifications indicating whether ports support USB 3.1/3.2 speeds, power delivery capabilities, and other advanced features relevant to your use cases.
Don’t assume that all USB-C ports on a device offer the same capabilities. Many devices feature different port configurations optimized for different use cases, such as charging-optimized ports versus data transfer-optimized ports.
Compatibility Planning for Multi-Device Setups
Consider your entire device ecosystem when making purchasing decisions. Ensure that new devices will integrate well with your existing peripherals, storage devices, and accessories, or factor in the cost of necessary adapters and replacements.
Plan for future expansion by choosing devices and accessories that support the full capabilities of USB-C and USB 3.1, even if you don’t immediately need all features. This approach provides flexibility for future use cases and ensures longer device relevance.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Connectivity
USB Type-C and USB 3.1 represent more than incremental improvements in connectivity technology – they constitute a fundamental shift toward more efficient, versatile, and user-friendly solutions that address the complex connectivity needs of modern digital life.
The combination of USB-C’s physical convenience and USB 3.1’s performance capabilities creates a platform that supports current applications while providing the flexibility and capability needed for future technological developments in type c technology .
As these standards continue to mature and gain adoption, users who embrace them early will benefit from simplified connectivity, improved performance, and better integration with the broader technology ecosystem. The transition may require some initial investment and adjustment, but the long-term benefits far outweigh the temporary inconveniences.
The future of connectivity is built on the foundation of universal standards that prioritize user convenience, performance, and compatibility. USB Type-C and USB 3.1 technologies represent significant steps toward that future, making them essential considerations for anyone seeking to optimize their technology experience.
Whether you’re a casual user seeking simplified charging solutions or a professional requiring high-performance data transfer capabilities, understanding and leveraging these modern connectivity standards will enhance your technology experience and prepare you for future developments in the ever-evolving digital landscape.

