Have you ever been standing in an electronics shop and seen usb cables that say USB-C and USB 3.0 cables and were unsure which one you should buy because you know you need one, but are unsure which? Such confusion has seen millions of consumers purchase the incorrect cables, receive slower-than-anticipated transfer speeds, or even break their machines with incompatible cords that cannot effectively transfer data.

This is the key that retailers are not always ready to disclose to you on the first page: USB-C and USB 3 are not technologies competing with each other; they are completely different ones with the focus on backwards compatibility. USB Type-C connector is defined by USB-C as the physical connector shape and USB 3 as the data transfer protocol.
We shall now proceed to clear up the record here in this comprehensive guide. You will understand why your so-called high-speed USB-C cable might not be as fast as an older USB connection, how to find out when a cable is actually fast, and what to look for when buying your next connection device, USB Implementers Forum. The outcome will be that henceforth you will not be cheated on product description anymore, and you will not squander your money on accessories that do not suit your product usb in case.
Understanding the Fundamental Difference: Physical vs Digital

The biggest mistake in the context of modern connectivity is the understanding of USB-C and USB 3 as the same. This has been brought about by the fact that marketing materials usually mix up hardware and software specifications, confusing different USB capabilities usb standards.
USB-C is entirely physical–it’s the type C connector, a reversible, small, oval-shaped connector that you can insert in any direction. Think of it as the “shape” of the plug, and remember that the USB-C is a reversible plug. USB connectors are of various physical formats, just as electrical outlets are rounded, flat, or three-prong shaped.

USB 3, though, is all about performance; it is also a data transmission standard that dictates the speed at which data will travel between your devices. Various iterations of this set of performance standards exist, including USB 3.0, USB 3.1, and USB 3.2, with the speed of each set of performance standards increasing accordingly as the USB Type-C ports.
Why This Confusion Matters for Your Wallet
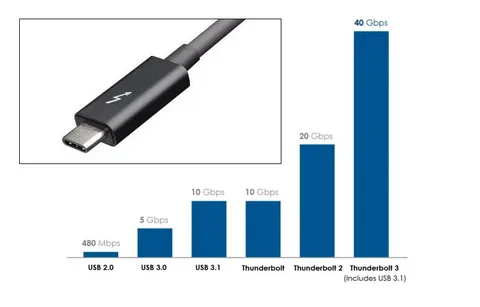
It is not just a difference in technical jargon, and it directly affects your purchase, as well as the functionality of your purchasing device. They can actually use the existing USB 2.0 protocol, so your shiny new cable might be able to transfer data painstakingly slowly at 2000 universal serial bus.
A more aged-looking USB-A connector, however, can be in a position to achieve lightning-fast USB 3.2 speeds. The connector is not even telling you how well you are really going to do based on the physical appearance of the connector multi lane operation.
USB-C: The Revolutionary Connector Design

USB-C is the largest advancement in connector design since the launch of the first USB in the 1990s. This tiny and symmetrical connector fits an amazing range of features in a space that is barely the size of a micro-USB port USB storage.
The reversible design removes the frustration that comes with towing the cables the correct way. Whether you are struggling to find the charging cord in the dark or just need to have a device connected within a few seconds, USB-C will always work, no matter what the position is, both USB-C.

Key USB-C advantages include:
- Revertable insertion (no longer need to flip the cable 3 times)
- Compact size suitable for thin laptops and tablets
- Support for multiple protocols simultaneously
- Universal compatibility across device types 1
- 0,000 or more inserts rated to survive.
The Power Revolution: What USB-C Can Really Do

Other than convenience, the true innovation of USB-C is its flexibility. One USB-C port can support data transfer, video output, audio transmission, and power delivery- all at the same time data transfer rate.
There are excellent power delivery capabilities. Normal USB-C has the potential to supply up to 100 watts, which is sufficient to power most laptops. Newer specifications raise this to 240 watts, enough to support high-performance gaming laptops and even desktop workstations up to two lanes.
This charging capability is the reason why most of the laptop manufacturers have been leaving USB-C as the charging port. Users can potentially have everything on one USB-C connection, as opposed to having to carry (and maintain) the separate power adapters, data cables, and video cables for electronic devices.
USB 3: The Speed Standard That Actually Matters

USB-C is news, due to its sleek design, but it is the USB 3 protocols that will dictate whether your data transfer will be over within just a couple of seconds or will take you a few minutes to transfer your information. This understanding of the USB connector, as well as the USB Type-C specification, is important in the context of choosing cables and equipment that meet your performance needs and connector specifications.
USB 3.0 (or SuperSpeed USB) is capable of speeds up to 5 Gbps (about 10 times the speed of USB 2.0). The latter speed is such that it allows moving large video files, creating entire libraries of photos, or even running applications on the external drive.
USB 3.1 Gen 1 is nothing more than USB 3.0; it is just a re-packaged brand that is confusing the market. In reality, the speed was doubled in USB 3.1 Gen 2, which increased its speed to 10 Gb.
USB 3.2 created even further complexity in addition to variants. Under ideal conditions, USB 3.2 Gen 1×1 can support 5 Gbps, and USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 can support 20 Gbps.
Real-World Speed Comparisons That Matter

Raw specification is not the whole story. In the real world, the speed of your actual transfers would be determined by a variety of factors, such as cable quality, capabilities of the device, and file type.
Real-world file transfers of USB 3.0 are often 300-400 MB/s. USB 3.1 Gen 2 is capable of reaching 800-900 MB/s when conditions are good. These are the speeds that will determine the difference between a 10-minute backup and 2 hours of hell.
These speeds do, however, demand compatible hardware on both sides, as well as considering the connector type. When using a USB 3.2 device, connecting it to non-compliant cables or a USB 2.0 port decreases the performance to USB 2.0 speed, no matter how good the cable is.
The Compatibility Maze: What Works With What

The compatibility issue is more of a frustrating element than any other pertaining to the USB technology. The advantage of all this is that USB protocols are generally backwards compatible, with newer versions generally being compatible with older devices, but at a reduced speed.
It is more complex as a matter of physical compatibility. USB-C can only use USB-C plugs. Earlier USB-A receptacles cannot be connected without adapters or special cables with alternative connectors on each end.
The protocol compatibility is not under similar rules. The device built on USB 3.0 will be usable on a USB 3.2 port, but at a speed of USB 3.0 only. The system will automatically negotiate as fast as the two devices can negotiate.
Adapter Challenges and Solutions
Adapters solve physical compatibility problems and introduce a few new problems. Cheap adapters will not be able to support everything USB-C has to offer, limiting the power output or data transfer speed.
Quality adapters maintain the signal integrity and deliver the full feature set, without compromising it by introducing cost and possible failure points. Where practical, the inherent compatibility of equipment and cables reduces complexity and enhances reliability.
Power Delivery: More Than Just Charging

The power delivery of USB-C goes way beyond charging devices. USB Power Delivery (USB PD) provides devices with the ability to negotiate power requirements in a dynamic manner.
A USB-C hub may require 15 watts of power to operate its internal electronics, and at the same time, provide 85 watts of power to a laptop connected to it. This smart power control allows complex arrangements with several devices sharing power from one source.
Power delivery profiles include:
- 5V/3A (15W) for smartphones and small devices
- 9V/3A (27W) for tablets and small laptops
- 15V/3A (45W) for ultrabooks 20V/3A (60W) for larger laptops
- 20V/5A (100W) for high-performance systems
Video and Audio Capabilities
USB-C has the capability of transporting video over the DisplayPort Alt Mode or Thunderbolt protocol. This allows single-cable external monitor solutions without the use of additional video cables.
Both analog and digital signals are supported by audio. USB-C headphones may be fed with high-quality digital audio streams, with adapters also providing support for 3.5mm headphones of the old type.
These multimedia features make USB-C exceptionally useful to mobile employees who require connecting to multiple display and audio setups during their daily routine.
Common Buying Mistakes to Avoid
Assuming that all USB-C cables have the same performance is the most costly error. A $5 USB-C cable could have a maximum speed of USB 2.0 and maximum power delivery of just a few watts, whereas a correctly specified full-featured USB cable costs $15-25 and provides maximum capability.
Red flags when shopping:
- Cables that are not specified by protocol, just by USB-C.
- Very low prices that look too good to be true.
- Lack of safety certification (UL, CE, FCC).
- Vague speed claims like “high-speed” without specific numbers
- No mention of power delivery capabilities
Reading Cable Specifications Correctly

Both connector type and protocol support are obviously stated by quality manufacturers. Look for labels like “USB-C to USB-A, USB 3.1 Gen 2, 100W PD support.”
This labeling informs you of the physical connector, the maximum data speed, and the amount of power that the connector can deliver. Any product that does not specify all these important features should be avoided.
Essential specifications to verify:
- Physical connector types on both ends
- USB protocol version (3.0, 3.1, 3.2)
- Power delivery rating in watts
- Cable length (longer cables can also be deployed)
- Safety certifications
Performance Optimization Tips

To achieve the highest possible USB performance, you want to pay attention to the overall signal path. The most sluggish element is the factor that defines the general performance, and thus, the increase in speeds of only one cable may not contribute to the increase in the speeds of other parts, which are already old.
Performance factors include:
- Host device USB controller capabilities
- Cable quality and length
- Destination device interface speed
- Background system activity
- File system types and fragmentation
Future-Proofing Your Setup
Technology changes fast; however, by selecting quality constituents with room to grow, you are sure to save on your investment. USB 3.2 Cable is a little more expensive than USB 3.0, but it offers a lot more features as you upgrade hardware.
USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 are the next generation, which will be even faster and have more features based on USB-C connectors. You can be ready now by investing in USB-C infrastructure that is ready to support standards like USB 3.2 Gen 2.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

Slow transfer speeds are usually caused by a mismatch of protocols and not defective hardware. Make sure that the device and the cable can support the anticipated version of USB and that the cable is compliant.
Issues of charging are often due to low power delivery ratings. Make sure your cable and charger can support the wattage of what you need to charge at the fastest rate.
Connection instability could be a sign of bad connectors or bad cable quality. Gold-plated contact premium cables and strong strain reliefs are longer-lasting and have better connections.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs

The combination of features and cost that best fits your particular usage scenario is defined by your specific use case. The simplest data transfer and charging a device do not need the same capabilities as professional video editing or an external drive array.
For basic users: USB-C cables with USB 3.0 support and 60W power delivery handle most common tasks affordably.
For power users: USB 3.1 Gen 2 or USB 3.2 cables with 100W+ power delivery support professional workflows and future device upgrades.
To use specialized applications: Thunderbolt 4 cables or USB4 cables offer the highest level of performance, but are much more expensive than their standard counterparts.
The Bottom Line: They Work Together
USB-C and USB 3 are not competing technologies anymore; they are two sides of the new connection. The best solution is one that combines the physical usability of USB-C and the USB 3 high-performance features.
Understanding this relationship will also help you to make good choices when purchasing products and remove the doubt that is the cause of buyer’s remorse. Whether it is smartphones, laptops on the go, or even transferring very large files, a combination of both connector and protocol will give optimum performance and value.
NB: When buying something USB-related, never forget to check the type of physical connector and the data protocol specifications. This small activity will not only save you time and money but also frustration, too and ensure your machines are doing what they are capable of doing.

