Introduction
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) cables have become the unsung heroes that power our digital lives in the present day highly connected world. Whether it is to charge your smartphone or transfer files between two machines, USB connectors offer a fantastic level of efficiency in a range that includes accessing different data and power transmission, with different colors for easy identificat . With the influx of USB variants, such as the typical rectangle USB-A and the game-changing reversible USB-C,debugging the internal setups and identifying color codings is more important than ever.
If you are struggling to fix a broken cable, choosing the correct connector to use in the project or just wondering about modern technology used to facilitate connectivity, then this guide will demystify USB cable wire color codes, including different colors, and help you navigate the maze of connectivity standards.
What you’ll discover:
- Inward system of wire colour coding to all forms of USBs
- How USB cables are able to transfer both data and power?
- USB 1.0 to the latest USB 4 technologies
- The advantage of Lightning port Connection to USB-C advantages
- Details of what to consider when selecting the right cable to use.
What Is a USB Cable?

USB technology was developed in the mid-1990s as an innovative breakthrough to standardize all connections necessary to peripherals in order to get rid of the mess of proprietary ports that had so bedeviled early computing. This standardized connection made the way we attach keyboards, mice, printers and later on smartphones uniform by using a common vocabulary in device communication.

Underlying the data and power-carrying capacities of any USB cable, therefore, are two basic functions: data transfer and power delivery. This two-way connection permits a single cable to charge and concurrently sync photos, or power an external hard drive and read and write files. This is made possible by the internal wire color coding system, also referred to as the wire color code for usb cable wherein there are computer specific colors that determine power wires and data transmission in all versions of USB and connector type.
How Do USB Cables Work?
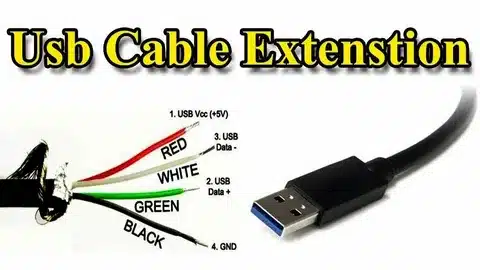
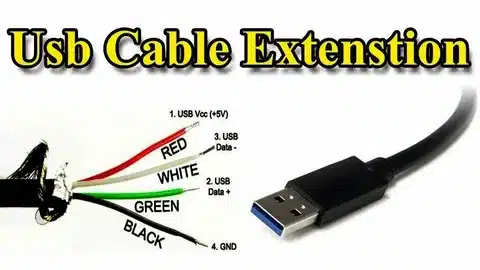
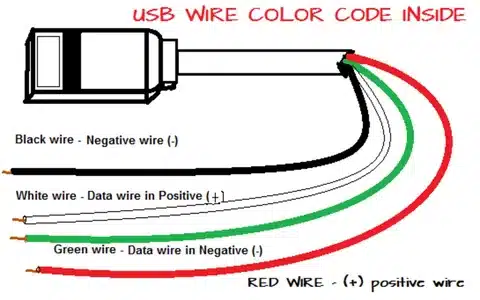
USB functionality is a well kept secret in which internal wiring has been given more precision usb specification. All standard USB cables have four wires inside, including three wires assigned a particular color code:
Power Wires:
- Red wire (VBUS): Supply of 5V DC power by the host to device
- Black wire (Ground): Black, gives electrical ground/return path
Data Wires:
- Green wire (D+): positive transmission of data
- White wire (D-): Negative signaling transmission of data
This color system is universal regardless of the USB version under consideration, including the usb ports be it a simple USB 2.0 connector or a high-speed USB 3.0 transfer response. The data wires are a plucked pair that allows utilizing differential signaling that inhibits electro-magnetic interference and allows reliable data transmission over greater distances, even at the opposite end of the connection positive data.
In USB 3.0 and later standards other wire pairs are added used to support the higher speed, but the underlying color scheme is the same red-black-green-white color scheme previously mentioned and basic functionality continues to depend upon those four wires hi speed.
USB Versions Explained

With each successive generation, USB technology has grown steadily and adhered to the usb standard , yet, remained backward-compatible:
| USB Version | Release Year | Maximum Speed | Key Features |
| USB 1.0 | 1996 | 1.5 Mbps | Initial standard, basic connectivity |
| USB 1.1 | 1998 | 12 Mbps | Improved reliability, widespread adoption |
| USB 2.0 | 2000 | 480 Mbps | High-speed data transfer, became dominant |
| USB 3.0 | 2008 | 5 Gbps | SuperSpeed, improved power delivery |
| USB 3.1 | 2013 | 10 Gbps | Enhanced SuperSpeed, USB-C introduction |
| USB 3.2 | 2017 | 20 Gbps | Multi-lane operation, faster charging |
| USB 4 | 2019 | 40 Gbps | Thunderbolt 3 compatibility, ultimate performance |
It is the beauty of USB since its designing because USB 4 port has the capability to support the USB 2.0 device but performance will be set according to the capabilities of the older standard. This will make sure that your legacy equipment will continue to work despite the change in the technology.
USB Connector Types: From Lightning Port to USB-C
Knowledge of connector types is pivotal to picking the proper cable, particularly in the Lightning connector vs USB-C matchup or indeed a working iPhone USB-C huawei supercharge:
USB Type-A: The rectangular plug pronounced and used on the computers, wall chargers, and power banks. The familiar design has also not changed much ever since the introduction of USB and that makes it easily identifiable by everyone yellow.
USB Type-B: The box-shaped connector mostly used with printers, scanners and external hard drives. Not commonly used in consumer electronic but necessary in professional equipments.
USB Type-C: This is taking the world by storm, the newest standard with a reversible connector, and fast becoming the standard connector. USB-C supports the maximum of 100W of power delivery and 40 Gbps data transfer; it is the future. The Apple charging port switch to USB-C proves how the connector is universal.
Mini-USB: Mini-USB was once a popular connector in digital cameras and early smartphones, superseded by more-efficient options.
Micro-USB: The once ubiquitous smartphone standard, still present on some budget phones, fitness trackers and accessories. In USBs 2.0 and 3.0.
Lightning (Apple): Apple-endorsed reversible connector on the iPhones and the iPads. Its closed system which brings with it the beauty and reliability is, however, disadvantaged by its closed ecosystem limiting its compatibility with open standards, affecting certain charging devices .
USB-C benefits are strong: reversible plug and port design, compatibility with all manufacturers, and the ability to support all data, power, and video transmissions, in a single port.
Backward & Forward Compatibility
The most significant strength is that BP is focused on generation compatibility. A USB 3.0 gadget will be usable in a USB 2.0 port, but at USB 2.0-performance. This backward compatibility makes the upgrading of the computer not render it obsolete to using the existing peripherals.
To USB-C transition, adapters can act as an interchange that is a bridge between old and new technologies. With a USB-C to USB-A cable, new laptops can be used with older devices and USB-C to Lightning cables mean that iPhone owners can use faster charging abilities.
The important rule is that performance defaults within the chain of connections to the lowest common denominator. An example is a USB 2.0 device connected using a USB 3.0 cable to a USB 3.0 port will run at USB 2.0 speeds.
Choosing the Right USB Cable
To choose the best USB cable, it is paramount to consider a number of key hardware issues.
Use Case Identification :Do you require the cable to charge, transfer data or to output video? The faster rate of data transfer demands newer USB 3.0 or higher, including the handling of negative data but a standard charge does not need anything more than USB 2.0.
Connector Compatibility: Both ends must have the same compatibility of their ends to your devices. The ascendency of USB-C leaves a large number of users with a need to have cables with a combination of connector types during transition.
Speed Requirements: Select a USB version, according to your requirements. USB 3.0 speeds are useful when transferring files, but regular device charging does not need the newest standard.
Cable Length Considerations: Physics matters – The USB 3.0 spec has a maximum cable length of 3 meters to assure best performance, USB 2.0 can go as long as 5 meters. The longer distances need active cables or hubs
Build Quality Matters: Quality of connectors, materials (such as braided exteriors) and shielding, including the ground wire, are all important factors to consider. Higher quality cables will endure longer and connection is more dependable.
Safety Certifications: Look at USB-IF (USB Implementers Forum) certification and safety requirements such as UL listing. Hack Uncertified cable aka cheap cables are harmful to the devices or could lead to safety hazards.
Environmental Responsibility: Select manufacturers who have environmental responsible processes that utilize proper recycling needs of the end-of-life cables, including considerations for the ground wire .
Frequently Asked Questions
What is USB On-The-Go (OTG)? Definition of USB On-The-Go (OTG). With TG, mobile devices can be hosts, and smartphones can interact with USB drives, keyboards or mice without the use of a computer as mediator.
Which cables support fast charging? High power delivery Cables compatible with fast charging need to be rated at higher power. USB-C cables have a higher power capacity of up to 100W as opposed to USB-A, which usually stop at 12W. Never blindly assume that charging specification of your device
Are USB ports color coded? Yes! USB ports are commonly color coded: white is used to denote USB 1.0/ 1.1, black denotes USB 2,0, and blue ports are used to indicate USB 3.0, and teal denotes USB 3.1/3.2.
What are the maximum cable lengths? USB 2.0 can provide up to 5 meters, USB 3.0 can provide only up to 3 meters, and USB-C can vary depending on implementation, but in general it will be limited to USB 3.0+ limits in data applications.
Can I use any USB-C cable for everything? USB-C cables are not all created equal. Some can only charge, some transfer data and some have power to charge high-speed video output.
Quick Reference Guide
USB Wire Color Code:
- +5V Power: (VBUS)
- Black: Ground
- Green: Data Positive (D+)
- White: Data Negative (D-)
Connector Quick ID:
- Rectangular = USB-A
- Square = USB-B
- Oval, USB-C reversible
- 9-pin – Micro-USB
- Lightning and Apple 8-pin are equal.
Safe Disposal Tips:
- Check local recycling schemes on recycling local electronics
- A lot of retailers tend to recycle cable
- Ensure that you do not take cables out of their original packaging and put them in the bin because cables can be recycledlag
- You have working, functional cables that you want to get rid of, think about donating them to schools or community centers
Conclusion
Knowledge of the USB cable wire color codes and connector types equips you with the ability to make right choices when it comes to your connectivity requirements, and the right answer to common question . Knowledge of this background allows the core red-black-green-white wiring scheme used in all USB connections, to the complex capabilities of USB-C technology is optimised to provide both perfect device performance and safety.
With technology progressing towards a world of universal USB-C connectivity, understanding the concepts contained in this guide can provide you guidance on how to navigate the change whilst remaining compatible with older equipment. Be it an upgrade to USB-C iPhone or a simple worn cable replacement you can now make a confident decision.
Note: quality should not be compromised when it comes to cables. Invest in quality-built, certified cables that are suited to the level of performance and safety in accordance with the demand.